As quantum computing threats emerge, organizations are adding quantum key distribution (QKD) systems as part of their strategy for quantum resilience. The differing protocols create operational complexity and limit deployment scalability between different QKD implementations.
Phio TX® by Quantum Xchange addresses these challenges through orchestration that bridges Cisco’s Secure Key Integration Protocol (SKIP) and the ETSI GS QKD 014 standard. This enables network administrators to deploy quantum-safe networking solutions with enhanced availability, fault tolerance, and multi-protocol support.
This article covers multi-protocol issues and orchestration capabilities in Phio TX.
The QKD Protocol Challenge
Multiple QKD protocols exist, creating vendor-specific implementations that cause interoperability challenges. Modern enterprise networks require seamless integration between QKD systems and existing infrastructure while supporting high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability across diverse network topologies.
Protocol Definitions
Cisco Secure Key Integration Protocol (SKIP)
Cisco’s SKIP enables any Cisco router supporting encryption to use keys from quantum distribution systems, allowing routers to securely import post-quantum pre-shared keys (PPK) from external sources like QKD devices.
Key Characteristics:
- HTTPS-driven protocol designed for seamless Cisco routing infrastructure integration
- API enabling network devices to obtain quantum-safe keys from external key management systems
- Multiple security layers, including authentication, secure transport, and integrity verification
- Compatible with any encryption-capable Cisco router without specialized hardware modifications
ETSI GS QKD 014 Standard
ETSI GS QKD 014 defines the “Protocol and data format of REST-based key delivery API” for quantum key distribution systems, specifying communication between clients and QKD modules to retrieve cryptographic keys exchanged using QKD protocols.
Key Characteristics:
- Vendor-neutral specification enabling interoperability between different QKD implementations
- RESTful API architecture accessible to a wide range of client applications
- Requires mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication for strong security
- Supports multi-user environments and enterprise-scale deployments
- Designed for integration with various network architectures, including 5G/6G technologies
The Interoperability Problem
Protocol Incompatibility
SKIP and ETSI GS QKD 014 protocols create operational challenges:
- API Differences: Different API structures, authentication mechanisms, and data formats
- Key Format Variations: Different key formats, metadata structures, and delivery mechanisms
- Authentication Models: Different authentication approaches create policy consistency issues
Operational Complexity
Without orchestration, organizations face:
- Multiple Management Interfaces: Different configuration requirements and operational procedures
- Limited Scalability: Protocol incompatibilities restrict large-scale, heterogeneous QKD networks
- Fault Tolerance Limitations: Complex high availability implementation across different protocols
Phio TX Overview
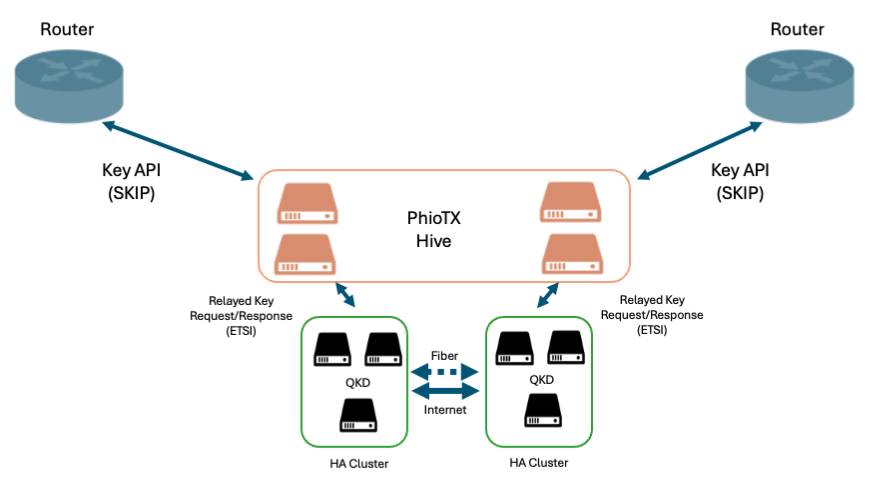
As a part of orchestration functionality, Phio TX addresses multi-protocol QKD deployment challenges. The solution, deployed in a mesh called a Hive, acts as intelligent middleware that normalizes protocol differences and provides unified key management services.
Figure 1: Multi-protocol architectural diagram
Core Functionality:
- Protocol Translation: Real-time translation between SKIP and ETSI GS QKD 014 protocols
- Key Management Orchestration: Centralized key lifecycle management and distribution
- High Availability Coordination: Multiple QKD system cluster management
- Network Abstraction: Unified interface to network applications and management systems
Key Benefits and Features
- Consistent Key Distribution: Routers receive the same key that QKD systems return, regardless of underlying protocol. This ensures synchronization across distributed network elements and identical key material for encryption operations.
- Active-Active Clustering: Multiple QKDs in HA cluster operate actively using round-robin load distribution, maximizing resource utilization while scaling key generation capacity with participating systems.
- Uninterruptible Key Supply: Phio TX provides QKD fault tolerance, ensuring continuous quantum key availability for network encryption. The platform maintains key buffers and implements intelligent failover mechanisms, preventing service interruptions.
- Dynamic Key Bridge: Provides on-the-fly key conversion and protocol bridging between SKIP and ETSI GS QKD 014 formats, enabling mixed-vendor QKD infrastructures while maintaining protocol compatibility across all network elements.
- Network Extension Capabilities: Addresses traditional QKD distance limitations by enabling key relay and distribution across extended network topologies through multi-hop key distribution architectures.
- Resource Pooling: Orchestrating multiple QKD systems creates pooled resources where individual system failures don’t impact overall service availability, with automatic capacity scaling as new systems are added.
- Universal Compatibility: Supports both SKIP and ETSI GS QKD 014 protocols simultaneously, enabling organizations to leverage different QKD vendors without protocol compatibility constraints.
- Different API Support per Network Leg: Allows different APIs at each network leg, providing maximum flexibility for different network segments to access quantum keys based on specific requirements.
Use Cases
- Enterprise Data Center Interconnect: Implement quantum-safe encryption for inter-site connectivity with consistent key distribution across WAN links and fault tolerance through multiple QKD systems.
- Service Provider Networks: Offer quantum-safe services to enterprise customers while maintaining operational efficiency across diverse QKD infrastructure with simultaneous multi-customer protocol support.
- Government and Critical Infrastructure: Ensure the highest security levels while maintaining operational flexibility, supporting compliance with security standards and integration with existing security infrastructure.
Conclusion
Phio TX by Quantum Xchange addresses critical interoperability challenges for QKD technology adoption in enterprise networks. By providing seamless integration between Cisco SKIP and ETSI GS QKD 014 protocols, Phio TX enables organizations to deploy quantum-safe networking solutions leveraging the best capabilities of different vendors while maintaining operational simplicity.
The solution’s comprehensive feature set includes high availability clustering, real-time protocol conversion, and flexible API support. This makes it essential for organizations implementing robust, scalable quantum-safe infrastructure. As quantum computing threats evolve, Phio TX provides the foundation for quantum-safe networking that adapts to changing requirements while maintaining the highest levels of security and availability.
This article covers multi-protocol issues and is part of a series on solving issues using orchestration capabilities in Phio TX.